|
ASP.NET Core 환경에서 예외 발생 처리 방법에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
특정 Controllers에서 각각 예외 처리를 하는 경우 예외 처리가 분산 처리 되어 논리적으로 예외 처리가 필요한 경우 중복 코드 발생 여지가 있으며, 관리하기 힘든 구조가 될 수 있습니다.
때문에 예외 처리 담당 Middleware 파이프라인을 구성해서 모든 요청에 대한 예외를 중앙에서 컨트롤하여 처리 하는 것이 좋습니다.
이번 내용에서는 커스텀하게 예외 처리를 하는 Middleware 를 직접 구현해 보고 .NET Core 이상 부터 기본 지원되는 UseExceptionHandler Middleware (Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.ExceptionHandlerMiddlewareImpl.ExceptionHandlerMiddlewareImpl) 를 사용하는 방법을 알아봅니다. 이 글에서 다루는 코드는 다음 Repository에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
code_check - ExceptionHandler
글로벌 예외 처리시 이점 (예외 중앙 처리 방식)- 예외 처리를 분산 시키지 않고 특정 한곳에서 예외 처리에 대해 논리적으로 처리 하고 관리 할 수 있습니다.
- 예외 처리를 미들웨어로 구현했을때 파이프라인 구성으로 원하는 처리 시점을 자유롭게 설계 할 수 있습니다.
- 모든 요청에 대한 오류 발생시 예외를 캐치하여 클라이언트에게 자세한 예외 메세지와 해결 방법을 제시하도록 설계 할 수 있습니다.
Custom Exception MiddlewareASP.NET Core 에서 클라이언트의 요청은 파이프라인 형태로 요청을 처리하는 Delegate의 시퀀스로 구성할 수 있습니다.
각 Delegate는 요청을 처리하고 클라이언트에게 응답할 수 있으며 중간에 예외처리도 가능합니다.
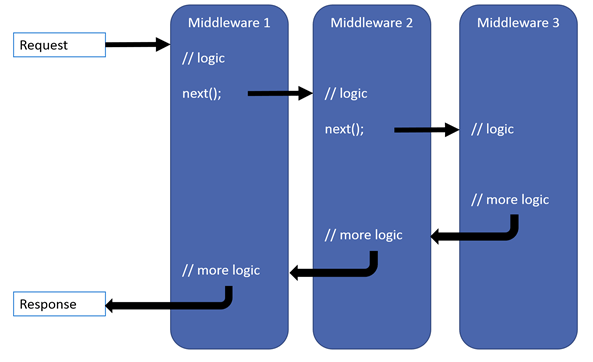
(ASP.NET Core 에서 Middleware 처리 동작 개념 다이어그램)
가장 먼저 직접 Middleware를 구현해서 클라이언트 요청 처리 도중 예외가 발생 되었을때 모든 예외 처리를 중앙에서 처리 하는 방법을 알아보겠습니다.
우선 예외 발생시 상세 예외 정보를 클라이언트에게 표시하는 목적의 모델을 다음과 같이 생성 합니다.
[Models/ExceptionDetails.cs]
namespace HandlingExceptions.Models;
using System.Text.Json;
public class ExceptionDetails
{
public int StatusCode { get; set; }
public string? Message { get; set; }
public string? DetailMessage { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return JsonSerializer.Serialize(this);
}
}
그리고 예외 처리 담당 Middleware를 생성 합니다.
[Middleware/ExceptionMiddleware.cs]
using HandlingExceptions.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Features;
namespace HandlingExceptions.Middleware;
public class ExceptionMiddleware
{
private const int DefaultStatusCode = StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError;
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private PathString _exceptionHandlingPath { get; set; }
private readonly RequestDelegate _exceptionHandling;
private readonly ILogger _logger;
public ExceptionMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
_logger = loggerFactory.CreateLogger<ExceptionMiddleware>();
_next = next;
}
public ExceptionMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory,
string? errorHandlingPath, RequestDelegate exceptionHandling)
{
_logger = loggerFactory.CreateLogger<ExceptionMiddleware>();
_next = next;
_exceptionHandlingPath = new PathString(errorHandlingPath);
_exceptionHandling = exceptionHandling;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext httpContext)
{
try
{
await _next(httpContext);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, ex.Message);
await HandleExceptionAsync(httpContext, ex);
}
}
private async Task HandleExceptionAsync(HttpContext context, Exception exception)
{
context.Response.StatusCode = DefaultStatusCode;
var exceptionDetails = new ExceptionDetails()
{
StatusCode = context.Response.StatusCode,
Message = "Error from middleware.",
DetailMessage = exception.Message,
};
if (_exceptionHandlingPath != null &&
_exceptionHandlingPath.HasValue &&
_exceptionHandling is not null)
{
context.Request.Path = _exceptionHandlingPath;
ClearHttpContext(context);
// HttpContext에 예외 정보 추가
context.Features.Set<ExceptionDetails>(exceptionDetails);
await _exceptionHandling(context);
}
else
{
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
await context.Response.WriteAsync(exceptionDetails.ToString());
}
}
private static void ClearHttpContext(HttpContext context)
{
context.Response.Clear();
context.SetEndpoint(endpoint: null);
var routeValuesFeature = context.Features.Get<IRouteValuesFeature>();
if (routeValuesFeature != null)
{
routeValuesFeature.RouteValues = null!;
}
}
}
코드를 살펴보면 예외 발생시 Uri를 리라우팅 해서 별도의 Error 요청 컨트롤러로 처리하는 용도와 ExceptionMiddleware 에서 바로 처리 하는 용도로 두개의 생성자가 정의되어 있습니다.
그리고 클라이언트 요청시 호출되는 InvokeAsync(HttpContext httpContext) 메서드 에서 예외 발생시 HandleExceptionAsync(HttpContext context, Exception exception) 메서드 로 호출되어 처리 되고 있습니다.
그리고 HandleExceptionAsync(HttpContext context, Exception exception) 메서드 에서는 예외 발생시 Uri 리라우팅 Middleware 호출로 처리될지 분기되고 있습니다.
이때 리라우팅 되는 경우 상세 예외 정보를 ExceptionDetails 모델에 설정해서 HttpContext에 추가 해서 라우팅 미들웨어로 요청 합니다.
위 처럼 구현한 ExceptionMiddleware를 Middleware로 등록해서 사용하면 되는데 저는 다음과 같이 확장 메서드로 간편하게 등록해서 사용할 수 있도록 처리했습니다.
[Extensions/ExceptionMiddlewareExtensions.cs]
using HandlingExceptions.Middleware;
namespace HandlingExceptions.Extensions;
public static class ExceptionMiddlewareExtensions
{
internal const string GlobalRouteBuilderKey = "__GlobalEndpointRouteBuilder";
internal const string UseRoutingKey = "__UseRouting";
public static void ConfigureCustomExceptionMiddleware(this IApplicationBuilder app, string? errorHandlingPath = null)
{
if(string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(errorHandlingPath) is true)
{
app.UseMiddleware<ExceptionMiddleware>();
}
else
{
app.Use(next =>
{
var loggerFactory = app.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredService<ILoggerFactory>();
return new ExceptionMiddleware(next, loggerFactory, errorHandlingPath, Reroute(app, errorHandlingPath!, next)).InvokeAsync;
});
}
}
internal static RequestDelegate Reroute(IApplicationBuilder app, string errorHandlingPath, RequestDelegate next)
{
var builder = app.New();
Func<IApplicationBuilder, IApplicationBuilder> useRoutingFunc =
(Func<IApplicationBuilder, IApplicationBuilder>)app.Properties[UseRoutingKey];
builder.Properties[GlobalRouteBuilderKey] = app.Properties[GlobalRouteBuilderKey];
useRoutingFunc(builder);
// ExceptionMiddleware 호출 미들웨어 적용
builder.Run(next);
return builder.Build();
}
}
Error 요청 전용 컨트롤러가 있는 경우 errorHandlingPath 파라메터로 해당 uri를 전달해주면 ExceptionMiddleware 미들웨어에서 리라우팅 용도의 미들웨어를 별도로 호출하도록 구현 했습니다.
참고로 리라우팅 처리 방식은 새로운 builder를 생성해서 기존 RouteBuilder 값을 설정합니다.
이렇게 생성된 builder를 라우트로 등록해서 리라우팅 설정을 합니다.
이러면 HttpContext.Request의 Path설정에 있는 uri경로로 라우트 됩니다.
(ExceptionMiddleware의 HandleExceptionAsync(HttpContext context, Exception exception) 메서드 내용중 context.Request.Path = _exceptionHandlingPath 참고) 참고로 이때 HttpContext의 EndPoint 설정을 제거 리라우팅 됩니다.
(ExceptionMiddleware의 ClearHttpContext(HttpContext context) 메서드 참고)
이제 다음과 같이 미들웨어를 등록합니다.
[Program.cs]
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseHttpLogging();
..[중간 생략]..
// Global Exception log 처리 미들웨어 등록
app.ConfigureCustomExceptionMiddleware("/Error2");
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
다음은 예외 테스트를 하기 위한 테스트 컨트롤러와 예외 발생시 요청을 담당하는 컨트롤러를 다음과 같이 구현 합니다.
[Controllers/ErrorController.cs]
using HandlingExceptions.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace HandlingExceptions.Controllers;
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class ErrorController : ControllerBase
{
[ApiExplorerSettings(IgnoreApi = true)]
[Route("/Error2")]
public IActionResult Error2()
{
var exceptionDetails = HttpContext.Features.Get<ExceptionDetails>();
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, exceptionDetails);
}
}
예외 테스트는 간단하게 다음과 같이 처리해 보았습니다.
[HttpGet("/TestException")]
public IActionResult TestException()
{
var i = 0;
return Ok(100 / i);
}
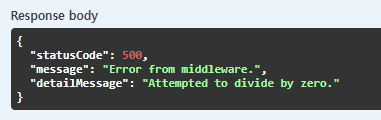
결과를 확인해 보면 다음과 같이 예외 발생시 ExceptionMiddleware 미들웨어를 통해 ErrorController 로 리라우팅 되서 처리 되는걸 확인해 볼 수 있습니다.
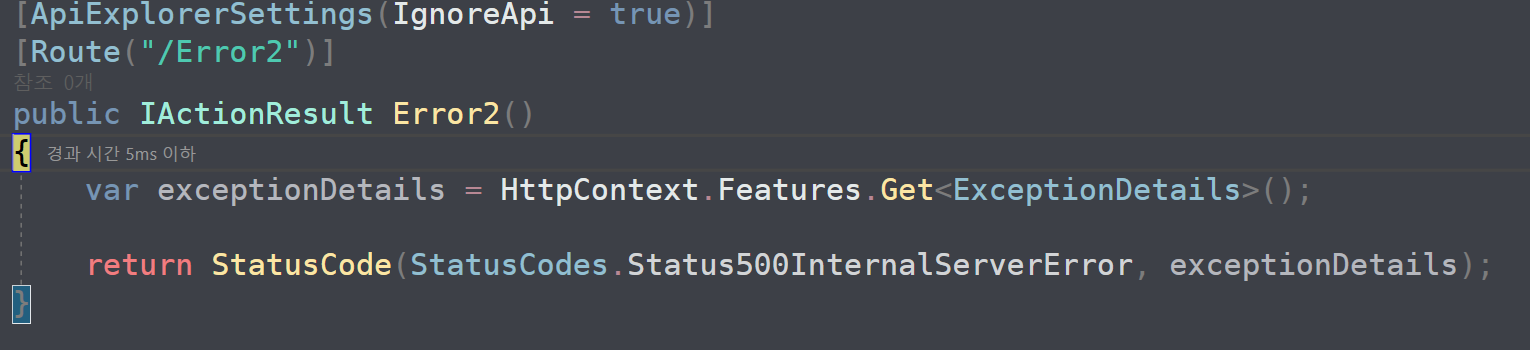
[응답결과]
 UseExceptionHandler지금까지 구현한 예외 처리 미들웨어는 .NET Core 에서 기본 지원되는 UseExceptionHandler 를 사용해서 간단하게 처리 할 수도 있습니다.
UseExceptionHandler 를 사용하면 내부적으로 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.ExceptionHandlerMiddlewareImpl.ExceptionHandlerMiddlewareImpl 미들웨어가 파이프라인 처리 되어 예외 처리를 할 수 있도록 구성해 줍니다.
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.ExceptionHandlerMiddlewareImpl.ExceptionHandlerMiddlewareImpl 미들웨어는 위에서 직접 구현해본 ExceptionMiddleware 와 동작 방식이 다음과 같이 100% 동일 합니다.
클라이언트 요청 처리도중 예외가 발생 되었을때 내부적으로 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.IExceptionHandlerFeature 인터페이스에 상세 예외 정보를 설정하고 HttpContext에 추가 합니다.
그래서 해당 값을 가져와 예외 처리를 할 수 있도록 제공해 줍니다.
UseExceptionHandler를 사용하려면 위에서 했던 작업과 동일하게 등록해주고 예외 발생 요청을 처리 컨트롤러에 리라우팅 되도록 설정할 수 있습니다.
[Program.cs]
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseHttpLogging();
..[중간 생략]..
// Global Exception log 처리 미들웨어 등록
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
}
그리고 예외 발생 요청을 컨트롤러도 다음과 같이 구현해 볼 수 있습니다.
[Controllers/ErrorController.cs]
using HandlingExceptions.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace HandlingExceptions.Controllers;
[ApiExplorerSettings(IgnoreApi = true)]
[Route("/Error")]
public IActionResult Error()
{
var context = HttpContext.Features.Get<IExceptionHandlerFeature>();
var exception = context.Error;
var problemDetails = new ProblemDetails
{
Status = StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError,
Title = "요청 처리중 오류가 발생 했습니다.",
Detail = exception.Message
};
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, problemDetails);
}
여러가지 예외 타입 처리 하기예외를 여러가지 타입 별로 다뤄야 하는 상황에서는 예외 발생 요청을 처리 컨트롤러에서 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.IExceptionHandlerFeature 의 Error 속성에 타입을 체크해서 타입별로 분기처리가 가능 합니다.
[ApiExplorerSettings(IgnoreApi = true)]
[Route("/Error")]
public IActionResult Error()
{
var context = HttpContext.Features.Get<IExceptionHandlerFeature>();
var exception = context.Error;
var problemDetails = new ProblemDetails
{
Status = StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError,
Title = "요청 처리중 오류가 발생 했습니다.",
Detail = exception.Message
};
// 401 예외 처리
if (exception is UnauthorizedAccessException) {
problemDetails.Status = StatusCodes.Status401Unauthorized;
problemDetails.Title = "권한 오류!";
}
return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, problemDetails);
}
지금까지 커스텀하게 미들웨어를 사용한 방식과 .NET Core에서 기본 제공 되는 UseExceptionHandler ( Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.ExceptionHandlerMiddlewareImpl.ExceptionHandlerMiddlewareImpl ) 를 사용해서 글로벌 하게 예외 처리 하는 방법을 알아 보았습니다.
위 코드는 다음 Repository에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
code_check - ExceptionHandler
|


